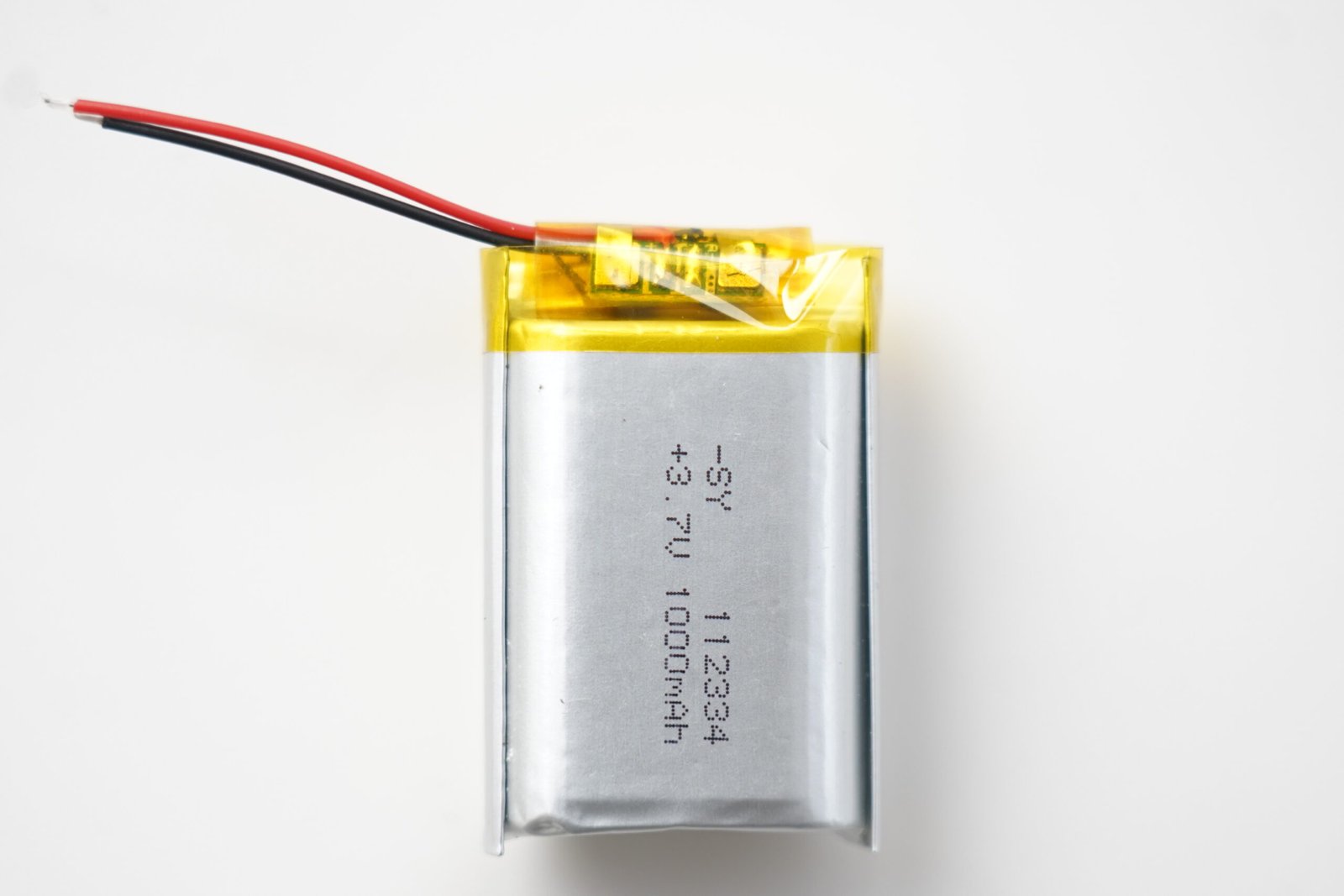
Lithium-ion polymer batteries are a cornerstone of modern portable energy storage, powering everything from wearables to drones with flexibility and efficiency.
A lithium-ion polymer battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses a gel-like or solid polymer electrolyte. It offers flexibility in design, lightweight construction, and excellent safety features.
Understanding how lithium-ion polymer batteries work and their unique advantages can help you make informed decisions for your devices.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are the key features of lithium-ion polymer batteries?

Lithium-ion polymer batteries are lightweight, customizable in shape, and feature robust safety systems, making them ideal for compact and modern devices.
These batteries are constructed with a flexible polymer electrolyte instead of liquid, enabling unique shapes and enhanced safety while maintaining reliable performance.
Dive deeper into what makes lithium-ion polymer batteries so adaptable:
1. Design Versatility
Lithium-polymer batteries offer unmatched flexibility. Thanks to their polymer electrolytes, manufacturers can create batteries in virtually any shape or size. This makes them perfect for devices like drones, wearables, and ultra-slim smartphones.
2. Lightweight Construction
Compared to lithium-ion counterparts, LiPo batteries are lighter, enhancing portability. Their weight-to-energy ratio makes them ideal for applications requiring mobility, such as RC vehicles and compact power banks.
3. Enhanced Safety
With gel-like electrolytes, LiPo batteries reduce risks associated with leaks and overheating. They also boast durable packaging that can withstand more stress compared to traditional battery casings.
How do lithium-ion polymer batteries work?

The working principle of lithium-ion polymer batteries combines innovation with simplicity, making them safe and efficient energy sources.
LiPo batteries rely on lithium ions moving between an anode and a cathode through a polymer electrolyte during charge and discharge cycles.
Dive deeper into the process:
- Electrolyte Composition: The polymer electrolyte, gel or solid, enables a safer energy transfer while reducing the risks of thermal runaway.
- Ion Movement: During charging, lithium ions migrate to the anode. On discharge, they travel back to the cathode, generating energy for your device.
- Custom Shapes: Thanks to their polymer structure, LiPo batteries allow unprecedented customization, creating opportunities for modern electronics.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of lithium-ion polymer batteries?
LiPo batteries excel in certain areas while having limitations in others, making them suitable for specific applications.
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Adaptable shapes for slim and modern gadgets.
- Safety: Reduced risks of leaks and overheating.
- Lightweight: Ideal for compact and portable devices.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: Higher production costs than lithium-ion batteries.
- Energy Density: Slightly lower energy capacity compared to lithium-ion.
- Maintenance: Requires more careful handling and specific charging systems.
Where are lithium-ion polymer batteries used?

From drones to smartphones, LiPo batteries power a variety of devices with their unique characteristics.
These batteries are favored for applications where lightweight and flexible designs are critical, such as wearables, drones, and power banks.
Common Applications:
| Application | Example Devices | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Devices | Smartphones, tablets | Lightweight, slim |
| Drones | Hobby-grade drones, RC vehicles | High performance |
| Wearables | Smartwatches, fitness trackers | Compact, safe |
| Power Banks | Portable charging stations | Flexible, durable |
How do LiPo batteries compare to lithium-ion batteries?

While both lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries have their strengths, they serve different purposes depending on application needs.
Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and cost-effectiveness, while lithium-polymer batteries prioritize safety, flexibility, and lightweight design.
| Feature | Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) | Lithium-Polymer (Li-Po) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | High | Moderate |
| Form Factor | Rigid | Flexible |
| Safety | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Affordable | Higher |
| Applications | EVs, laptops | Wearables, drones |
Conclusion
Lithium-ion polymer batteries provide unparalleled flexibility, lightweight construction, and safety, making them a standout choice for modern, compact devices. As technology advances, they continue to redefine portable power solutions.

